Asia-Pacific Forum on Science Learning and Teaching, Volume 16, Issue 2, Article 10 (Dec., 2015) |
Pre-service Science Teachers’ Attitudes towards Chemistry
In the present study, “attitudes towards chemistry” is a uni-dimensional construct. Pre-service science teachers’ mean score of the attitudes towards chemistry was 42.34 with standard deviation of 5.034. Since the minimum score for this instrument is 15.0 and the maximum score for this instrument is 75.0, the mean score of the participants’ attitudes towards chemistry could suggest that pre-service science teachers had medium level of attitudes towards chemistry.
Pre-service Science Teachers’ Misconceptions about Chemical Kinetics
Pre-service science teachers’ mean score of the chemical kinetics concept test was 37.35 (out of 100.0) with standard deviation of 13.3. This shows that pre-service science teachers had lower performance for the concept test. It suggests that pre-service teachers had misconceptions on some items. The misconceptions reflected by the distracters of the chemical kinetics concepts test items were the common misconceptions in a certain chemical kinetics topic.When pre-service teachers’ responses about Chemical Kinetics Concept Test were closely examined, most of the pre-service teachers had misconceptions
Table 1 shows the objectives of the questions and pre-service teachers’ misconceptions and their percentages.Table 1. Objectives of the questions and percentage of pre-service teachers’misconceptions on that question
Question Number Context
Correct Response (%)
Misconceptions and their rate*
1
identification of the catalyst in reaction
54.3
Mixed the catalyst with the reaction intermediate in a reaction mechanism/ 37.0%
2
Factors affecting reaction rate
67.9
The concentration of reactants/13.6%
3
rate equation
29.6
Reaction rate equals to the multiplication of reactants’ concentration/ 28.4%
7
the graph of the reaction rate versus time
14.8
The reaction rate is the time that reactants turn into products, reaction rate in a chemical reaction means the process of reactants to form products, reaction rate is an amount of substance that turns into product in a certain temperature and concentration/ 49.4%
8
the properties of endothermic and exothermic reactions.
35.8
In exothermic reaction, increasing the temperature decreases the rate of reactions/ 30.9%
8
the properties of endothermic and exothermic reactions.
35.8
In only endothermic reaction, increasing the temperature increases the rate of reactions/ 17.3%
10
the effect of catalyst on activation energy.
12.3
When catalyst is added to a reaction, only pathway with lower activation energy is available. Also, they confused with catalyst and negative catalysts/ 30.9%
15
reaction mechanism
35.8
When concentration increases, then the time of reaction process increases/ 27.2%
15
reaction mechanism
35.8
Activation energy does not affect the reaction rate/ 7.4 %
15
reaction mechanism
35.8
The fast step determines the reaction rate/ 17%
20
reaction mechanism
19.8
The difficulties related to what is the reaction intermediate and catalyst in a reaction mechanism/ 16%
20
reaction mechanism
19.8
Confused with the slow step determine the reaction rate/ 24.7%
*Misconceptions lower than 10 percent did not be mentioned in the table.
Descriptive measures of the Chemical Kinetics Concept Test and Attitudes toward Chemistry scores are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Descriptive measures of the Chemical Kinetics Concept Test and Attitudes towards Chemistry scores
Chemical Kinetics Concept Test
Attitudes toward Chemistry
n
Mean
Std. Dev.
Mean
Std. Dev.
Total
81
37,35
13,3
42,34
5,034
Correlation between Preservice Science Teachers’ Attitudes towards Chemistry and their Misconceptions about Chemical Kinetics
In order to determine the relationship between preservice science teachers’ attitudes towards chemistry and their understanding of chemical kinetics, first attitudes towards chemistry and understanding of chemical kinetics concept were plotted. The assumptions of the Pearson’s Product-Moment Correlation were checked. Both attitudes toward chemistry and the concept test scores were normally distributed. There are two outliers, but when these were extracted from the analysis, the result of the Pearson correlation did not change.
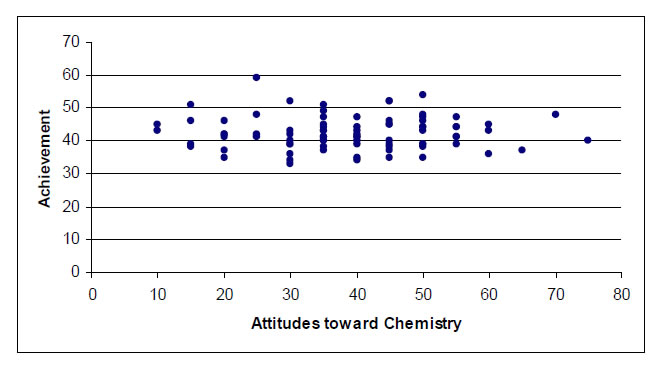
The graph showed that there is no linear relationship between attitudes toward chemistry and understanding of chemical kinetics. Figure 1 shows this relationship.
Figure 1. The relationship between attitudes towards chemistry and achievement.Since there is no linear relationship between variables, Pearson's Product-Moment Correlation was not implemented. The result demonstrated that there was not a significant correlation (r = 0.010) between pre-service teachers’ understanding of chemical kinetics and their attitudes towards chemistry.