Asia-Pacific Forum
on Science Learning and Teaching, Volume 10, Issue 2, Article 5 (Dec., 2009) |
Appendix A: Conceptual change text on the hydrolysis of salts
Question: The beakers above contain ammonium chlorine, sodium chlorine and sodium bicarbonate solution, respectively. What do you think about pH values of these salt solutions? Explain
Misconceptions: While many students believe that salt solutions are all neutral or have a pH of 7, some believe that they have not any value of pH or a pH of 0.
As you know, when salts dissolve in water they dissociate into their component cations and anions. The reactions of ions from salts with the water molecules to form H3O+ or OH- ions are called salt hydrolysis reactions.In the reaction, the water molecule takes part in the reaction as one of the reactants. From this, it is understood that salt solutions can be acidic, basic or neutral. If all salt solutions were neutral, pH at the equivalent point of all titrations would be 7. But we knows that pH at the equivalent points can be less or greater than 7. The reason for this is that a kind of salt formed.
Is it possible to predict whether a salt hydrolysis reaction produces an acidic solution (containing H3O+ ions) or a basic solution (containing OH- ions)?
The simplest way of this is to examine the acid and base from which the salt is formed. There are four possibilities: (i) salts of strong acids and strong bases: for example, NaCl is a salt formed by the neutralization reaction between NaOH and HCl.
The ions in NaCl solution are Na+ and Cl-. Both are the ions of a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH). Thus neither Na nor H3O+ hydrolyzes. A water solution of it is neutral and pH=7 at 25 0C, that is, neither acidic nor basic.
(ii) salts of strong acids and weak bases: for example, NH4Cl is a salt formed by the neutralization reaction between NH3 and HCl.
The water solution of this salt is slightly acidic or has a pH lower than 7 because the NH4+ ion donates H+ ions to water. This process is called salt hydrolysis. Because the Cl- is a conjugate base of HCl (a strong acid), it has not affinity for H+ ions. It is merely a spectator ion in this reaction
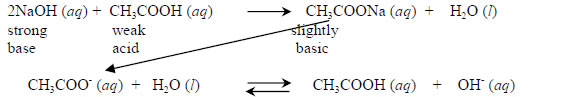
(iii) salts of weak acids and strong bases: solutions of these salts are basic and have a pH less than 7. For example, CH3COONa is a salt formed by the neutralization reaction between CH3COOH (weak acid) and NaOH (strong base).
Its water solution is basic because the CH3COO- (ethanoate) ion in the solution is a Bronsted-Lowry base and reacts with water to form ethanoic acid (acetic acid) and hydroxide ions. The Na+ ion is merely a spectator ion in the reaction.
and (iv) salts of weak acids and weak bases: Aqueous solutions of these salts can be neutral, acidic or basic depending on the relative strengths of the acid and base. In this case, both the cation and the anion of salt undergo hydrolysis. Whether salt solution is acidic, basic or neutral is estimated by comparing the values of Ka (the acid dissociation constant) and Kb (the base dissociation constant). If Ka(cation) > Kb(anion) the solution of the salt is acidic. If Ka(cation) = Kb(anion) the solution of the salt is neutral. If Ka(cation) < Kb(anion) the solution of the salt is basic. For example, if the base NH3 has a Kb = 1.6 x 10-5 and the acid HClO has a Ka of 3.4 x 10-8 , then the aqueous solution of HClO and NH3 will be basic because the Ka of HClO is less than the Ka of NH3.
In summary, if the acid is weak, i.e., poorly ionized and the alkali is strong, i.e., highly ionized, the aqueous solution of the salt will have an alkaline reaction as a result of the hydrolysis. In the opposite case, if the base is weak, the salt will have an acidic reaction in an aqueous solution.
Also, it can be decided from the molecular formulas of salts whether their water solutions are basic, acidic or neutral. Salts are made up of a cation (other than H+) and an anion (other than OH- or oxide, O2-). The formula of the salt indicates the acid and base that prepare the salt. The cation is derived from the base; the anion is derived from the acid. For example, let us predict whether a water solution of each of the following salts will be acidic, basic or neutral:
(a) NaCO3 is the salt of a strong base, NaOH and a weak acid, H2CO3. The Na+ ion will not hydrolyze but the CO3-2 ion will. A water solution of NaCO3 will be basic. (b) Na2SO4 is the salt of a strong base, NaOH and a strong acid, H2SO4. Neither the Na+ ion nor the SO4-2 ion hydrolyzes. A water solution of Na2SO4 will be neutral. (c) NH4NO3 is the salt of a weak base, NH3, and a strong acid, HNO3.The NH4+ ion will hydrolyze but the NO3-1 ion will not. A water solution of NH4NO3 will be acidic.
-- predict whether a water solution of each of the following salts will be acidic, basic or neutral: